curl -v --proxy-negotiate -u : https://blog.mydomain.com --proxy http://proxy.lan.local:3128
Wednesday, February 19, 2025
curl with auto negotiated proxy authentication
Friday, January 31, 2025
Synology: nginx(-proxy-manager) and rar2fs with docker
#!/bin/bash #NGINX mkdir -p /volume1/unpacked/rar2fs docker run --name nginx -v /volume1/unpacked/rar2fs:/usr/share/nginx/html:ro -p 5088:80 -d nginx:stable # NGINX-PROXY-MANAGER mkdir -p /volume1/docker/nginx-proxy-manager/data mkdir -p /volume1/docker/nginx-proxy-manager/letsencrypt docker run -d \ --name=nginx-proxy-manager \ -p 5080:80 \ -p 5443:443 \ -p 5081:81 \ -v /volume1/docker/nginx-proxy-manager/data:/data:rw \ -v /volume1/docker/nginx-proxy-manager/letsencrypt:/etc/letsencrypt:rw \ jc21/nginx-proxy-manager:latest #RAR2FS docker stop nginx docker stop nginx-proxy-manager docker stop rar2fs docker rm rar2fs mount --make-shared /volume1/ docker run \ -d \ --init \ --privileged \ --name rar2fs \ --cap-add MKNOD \ --cap-add SYS_ADMIN \ --device /dev/fuse \ --network none \ -v /volume1/stuff:/source \ -v /volume1/unpacked/rar2fs:/destination:rshared \ zimme/rar2fs docker start nginx-proxy-manager docker start nginx
Wednesday, January 22, 2025
Change password in RDP
There are some key combo’s like ctr-alt-end that might work in an RDP session. However, there are some scenario’s (e.g. with a Mac) that make it complicated.
Workaround:
C:\Windows\explorer.exe shell:::{2559a1f2-21d7-11d4-bdaf-00c04f60b9f0}
Thursday, August 22, 2024
Dump ssl keys with chrome for usage with Wireshark
"C:\Program Files\Google\Chrome\Application\chrome.exe" --ssl-key-log-file=%USERPROFILE%\Desktop\keylog.txt
Sunday, February 18, 2024
docker rar2fs on synology
If you do not want rar2fs to modify your files when opening, make sure /source is ro
docker run \ -d \ --init \ --name rar2fs \ --cap-add MKNOD \ --cap-add SYS_ADMIN \ --device /dev/fuse \ --network none \ --security-opt apparmor:unconfined \ -v /volume1/rarfiles:/source:ro \ -v /volume1/unrarred:/destination:rshared \ zimme/rar2fs
Tuesday, January 30, 2024
configure nginx
I want to use Certbot with Let’s Encrypt, but I don’t want my webserver to hand over the certificate to everyone knocking at my front door at poort 443.
Here’s how: I presume you have nginx and certbot installed.
Generate a self-singed certificate:
mkdir /etc/nginx/ssl/ sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.key -out /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.crt
Now use this certificate for the default listener. Also respond with a http 444 (empty reponse).
server {
server_name _;
listen 80 default_server;
listen 443 ssl default_server;
# sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.key -out /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.crt
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.key;
return 444; # no reponse
}
After that, all you have to do is create a file in /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/ e.g. blog.mydomain.com
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name blog.mydomain.com;
root /var/www/blog.mydomain.com;
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains" always;
}
Reload nginx.
Then run Certbot and follow the steps:
certbot --nginx --staple-ocsp -d blog.mydomain.com
Connecting with ssl without the proper host-header will now present the self-signed certificate and reponds with an empty reponse.
Wednesday, December 13, 2023
PL2303 usb-to-serial
For some reason this pl2303 won’t even work on linux and thus requires Windows.
Even then, you need this fix anno 2023.
Monday, July 31, 2023
Build specific php-apache docker image
So I don’t forget:
FROM php:8.0.29-apache # Update and install my default tools RUN apt-get update RUN apt dist-upgrade -y RUN apt-get install -y nano curl wget openssh-client net-tools # Enable RemoteIPHeader for Cloudflare Tunnels RUN a2enmod remoteip RUN sed -i 's/DocumentRoot \/var\/www\/html/DocumentRoot \/var\/www\/html\n\tRemoteIPHeader CF-Connecting-IP/g' /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default.conf # Set timezone RUN ln -fs /usr/share/zoneinfo/Europe/Amsterdam /etc/localtime RUN dpkg-reconfigure --frontend noninteractive tzdata
Monday, August 29, 2022
Chrome ERR_CERT_INVALID
I never knew….
If you cannot continue in Chrome because of an ERR_CERT_INVALID error, even after pressing Advanced: there’s a secret passphrase built into the error page. Just make sure the page is selected (click anywhere on the background), and type `thisisunsafe`
Sunday, July 24, 2022
ffmpeg reminder
Personal reminder:
Download latest: https://ffmpeg.org/download.html
Run ffmpeg -i MyMovie.mkv and look for stream info, e.g.:
Stream #0:0: Video: h264 (High), yuv420p(tv, bt709/unknown/unknown, progressive), 1920x800, SAR 1:1 DAR 12:5, 23.98 fps, 23.98 tbr, 1k tbn, 47.95 tbc (default) Stream #0:1(dut): Audio: ac3, 48000 Hz, 5.1(side), fltp, 448 kb/s title : Dutch Stream #0:2(dut): Audio: ac3, 48000 Hz, 5.1(side), fltp, 448 kb/s title : Flemish Stream #0:3(eng): Audio: ac3, 48000 Hz, 5.1(side), fltp, 448 kb/s title : English Stream #0:4(dut): Subtitle: subrip (default) (forced) Stream #0:5(dut): Subtitle: subrip Stream #0:6(eng): Subtitle: subrip
Say, I would like to have the video with the Flemish audio and all the subtitles (since they don’t take that much space)
ffmpeg -i MyMovie_2160p.mkv -vf scale=640:-2 -ac 2 -af "pan=stereo|FL=FC+0.30*FL+0.30*BL|FR=FC+0.30*FR+0.30*BR" -map 0:v:0 -map 0:a:1 -map 0:s MyMovie_640p_2ch.mkv
-vf scale=640:-2 = video filter: 640p, -2 means keep aspect ratio for vertical pixels -ac 2 = (convert to) 2 audio channels -af "pan=...... = audio filter: copy multichannel audio without losing center channel (dialogs) -map 0:v:0 = copy first (0) video stream -map 0:a:1 = copy second (1) audio stream (Start from 0. So 0 would be Dutch, 1 Flemish, 2 English) -map 0:s = copy all subtitles but if you have non-convertible subtitles (bitmapped), then first map the desired sub and copy, e.g.: -map 0:s:3 -c:s copy
Monday, July 11, 2022
ser2net p1 adapter yaml config
Because i didn’t make a backup. For next time’s reference:
connection: &p1usb accepter: tcp,10001 enable: on connector: serialdev,/dev/ttyUSB0,local,115200n81
Older ser2net, shipped with debian buster with ‘just’ a .conf file is easy:
10001:telnet:600:/dev/ttyUSB0:115200 8DATABITS NONE 1STOPBIT banner
Thursday, July 7, 2022
pfSense Multi VLAN DNS (host) overrides
pfSense’s DNS resolver has the ability to do host overrides from the gui, but these are global overrides.
Unbound (the underlaying DNS resolver) has the ability to create DNS views to do different things based on source addresses.
It is located under Services - DNS Resolver - General - Custom options. It is a free format field.
Example:
server: access-control-view: 10.123.12.0/24 vlan15activedirectory access-control-view: 10.158.1.0/24 vlan16guest view: name: "vlan15activedirectory" local-zone: "vpn.client.net" static # adding the host as a zone results in NXDomain lookup view: name: "vlan16guest" local-data: "vpn.client.net. 90 IN A 11.12.13.10" # adding a specific host and map it to a specific ip
More info: https://unbound.docs … ring/tags-views.html
Friday, March 18, 2022
Run powershell specific function from task scheduler
Executable is powershell.exe. Arguments:
-command "& { . "c:\location\to\script.ps1"; my_function_name }"
Powershell speed hacks
Powershell can be painfully slow when dealing with larger arrays, reading files and listing large directories. Here are some workarounds.
Arrays
Slow:
$myarray = @()
foreach ($x in $y) {
$myarray += $x
}
Much faster is working with an arraylist:
$myarray = [System.Collections.ArrayList]@()
foreach ($x in $y) {
$null = $procarray.Add($x)
}
Reading files
Slow:
get-content $filename
Fast:
([System.IO.File]::ReadAllLines($filename))
Listing large directories
Slow:
$items = get-item "\\server\share\*.csv" | sort LastWriteTime
The fastest workaround i’ve been able to find is actually using a dos prompt. Use dir switches for sorting purposes.
Note: dir returns just text, while get-items returns objects with all sorts of properties. It depends on your use case whether this hack is actually usable or not.
$items = cmd /r dir "\\server\share\*.csv" /OD /B
Tuesday, October 5, 2021
Install Windows 11 without TMP 2.0
When Windows 11 complains about your system not being compliant:
- press shift+F10
- regedit
- Navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\Setup
- new key: LabConfig
- new dword value: BypassTPMCheck = 1
- new dword vlaue: BypassSecureBootCheck = 1
Go back and resume the installation again.
Thursday, February 18, 2021
ESXi 7.0 U1 on a HP DL380p Gen8
Check your CPU here. Mine are Intel Xeon E5-2600 “version 0” series.
Download the HPE customized image
Does it work?
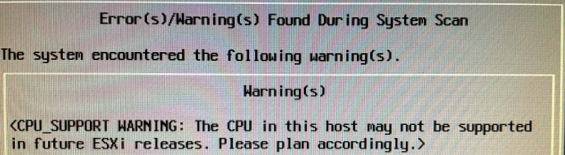
YES IT DOES.
According to the warning, the future is uncertain. But right now, 7.0 U1 is just fine!
Wednesday, February 10, 2021
Azure/O365/Teams authentication and monitoring bash curl scripts
Authorize for teams.
Replace YOUR_TENANT_ID, YOUR_EMAIL and YOUR_PASSWORD.
Use one of these client_id’s, depending on your usecase.
1fec8e78-bce4-4aaf-ab1b-5451cc387264 (Teams mobile/desktop application)
5e3ce6c0-2b1f-4285-8d4b-75ee78787346 (Teams web application)
auth.sh:
#!/bin/bash curl -s -X POST https://login.microsoftonline.com/YOUR_TENANT_ID/oauth2/token \ -c cookies.txt \ -o auth.blob \ -F grant_type=password \ -F resource=https://teams.microsoft.com/ \ -F client_id=1fec8e78-bce4-4aaf-ab1b-5451cc387264 \ -F username=YOUR_EMAIL \ -F password=YOUR_PASSWORD
This will save your bearer token, amongst others, to auth.blob in a json object.
Because the bearer token is only valid for a certain period of time, you’ll need to refresh it. Here’s how. You’ll need ‘jq’ installed to decompose the json object.
refresh.sh:
#!/bin/bash REFRESHTOKEN=`cat auth.blob | jq ".refresh_token" | sed 's/"//g'` curl -s -X POST https://login.microsoftonline.com/YOUR_TENANT_ID/oauth2/token \ -c cookies.txt \ -o auth.blob \ -F grant_type=refresh_token \ -F resource=https://teams.microsoft.com/ \ -F client_id=1fec8e78-bce4-4aaf-ab1b-5451cc387264 \ -F refresh_token=$REFRESHTOKEN
In the script you can keep repeating actions, but in order to keep your token active, you can use the following piece of code:
if [ -f "auth.blob" ]; then EXPIRES=`cat auth.blob | jq ".expires_on" | sed 's/"//g'` NOW=`date +%s` TTL=`expr $EXPIRES - $NOW` if [ $TTL -lt 60 ]; then echo "time for a refresh!" ./refresh.sh fi else echo "no previous auth present!" ./auth.sh EXPIRES=`cat auth.blob | jq ".expires_on" | sed 's/"//g'` NOW=`date +%s` TTL=`expr $EXPIRES - $NOW` fi
Now you can do the cool stuff like query your calendar or whatever:
#!/bin/bash
BEARER=`cat auth.blob | jq ".access_token" | sed 's/"//g'`
curl -s --write-out "%{http_code}|%{time_total}n" -o bla.txt "https://teams.microsoft.com/api/mt/emea/beta/me/calendarEvents?StartDate=2021-02-07T23:00:00.000Z&EndDate=2021-02-14T23:00:00.000Z" \
-H "User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Teams/1.3.00.30866 Chrome/80.0.3987.165 Electron/8.5.1 Safari/537.36" \
-H "authorization: Bearer $BEARER"
Or verify your local timezone:
#!/bin/bash BEARER=`cat auth.blob | jq ".access_token" | sed 's/"//g'` date "+%Y.%m.%e %T %N" curl -v 'https://teams.microsoft.com/api/mt/part/emea-03/beta/me/calendarEvents/timeZoneSettingsWithOffset?timezone=Europe%2FAmsterdam' \ -H "authorization: Bearer $BEARER" \ -H 'authority: teams.microsoft.com' echo "" date "+%Y.%m.%e %T %N"
Sunday, December 6, 2020
The Linux Desktop project
Since my work laptop is too restricted, i’m trying to set up Ubuntu on a USB stick and boot from there.
Actually, it has proven to be a very smooth experience so far. I’m impressed by the overall speed and battery performance.
Couple of things i must not forget.
WORK IN PROGRESS
Get some essentials:
sudo apt install curl ffmpeg keepassxc
Latest Google Chrome Browser: link
Latest Citrix Workspace (Receiver): link
Latest Citrix RTME (HDX for Skype): link
After installing the ica client:
sudo ln -s /usr/share/ca-certificates/mozilla/* /opt/Citrix/ICAClient/keystore/cacerts cd /opt/Citrix/ICAClient/keystore/cacerts sudo wget https://www.quovadisglobal.com/wp-content/files/media/quovadis_quovadisrootca2.pem sudo /opt/Citrix/ICAClient/util/ctx_rehash (for sectigo, go to https://support.sectigo.com/articles/Knowledge/Sectigo-Intermediate-Certificates, download the RSA OV bundle and do the same)
modify /opt/Citrix/ICAClient/config/wfclient.template before making the first connection (“~/Library/Application Support/Citrix Receiver/Config” on MacOS by the way)
MSLocaleNumber=0x00000413 KeyboardLayout=US-International
Also: modify /opt/Citrix/ICAClient/config/All_Regions.ini
MouseSendsControlV=False
If you use wayland and experience problems with special key-combo’s like alt-tab:
gsettings set org.gnome.mutter.wayland xwayland-grab-access-rules "['Wfica']" gsettings set org.gnome.mutter.wayland xwayland-allow-grabs true
For other apps: if you don’t know which value to use: xprop WM_CLASS
Lastly:
sudo apt-get install --reinstall libcanberra-gtk-module /opt/Citrix/ICAClient/util/configmgr (for mapping local drives)
Install Microsoft Teams:
sudo curl https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | sudo apt-key add - sudo echo "deb [arch=amd64] https://packages.microsoft.com/repos/ms-teams stable main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/teams.list apt update apt install teams
Connecting to exchange web services (for calendar sync)
sudo apt install evolution-ews
Google drive support e.g. for keepass
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:alessandro-strada/ppa sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install google-drive-ocamlfuse edit ~/.gdfuse/default/config and set mv_keep_target=true mkdir ~/Documents/GoogleDrive google-drive-ocamlfuse ~/Documents/GoogleDrive
startup file for google drive mount and offline backup of keepass databases:
#!/bin/bash google-drive-ocamlfuse ~/Documents/GoogleDrive if [ ! -d ~/BACKUP/keepass/ ]; then mkdir -p ~/BACKUP/keepass/; fi if [ -d ~/Documents/GoogleDrive/keepass/ ]; then cp -f ~/Documents/GoogleDrive/keepass/*.kdbx ~/BACKUP/keepass/; else echo Offline; fi
gedit json formatter:
Preferences - Plugins - enable External Tools
preferences - Manage external Tools
“+”, give name e.g. “Format Json”, shortcut key Ctrl+Alt+J, input=Current Document, output=Replace current document
code:
#! /usr/bin/env python import json import sys j = json.load(sys.stdin) print( json.dumps(j, sort_keys=True, indent=2) )
Kodi:
sudo apt-get install software-properties-common sudo add-apt-repository ppa:team-xbmc/ppa sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install kodi
Youtube-dl:
sudo curl -L https://yt-dl.org/downloads/latest/youtube-dl -o /usr/local/bin/youtube-dl sudo chmod a+rx /usr/local/bin/youtube-dl sudo ln -s /usr/bin/python3 /usr/local/bin/python
Wednesday, June 24, 2020
iptables log specific connections
Example how to allow certain known connections (e.g. unifi accesspoints) and log unknown connection attempts.
This is done by adding a chain called LOGDROP, append packets that match the criteria (tcp/8080) to that chain, log the packets and drop them.
iptables:
#!/bin/bash AP01="192.168.0.1" AP02="192.168.0.2" AP03="192.168.0.3" # Resetting ... iptables -P INPUT ACCEPT iptables -P FORWARD ACCEPT iptables -P OUTPUT ACCEPT iptables -F iptables -X # Setting default policy on incoming traffic iptables -P INPUT DROP # DENY INCOMING CONNECTIONS iptables -P FORWARD DROP # THIS IS NOT A ROUTER # allowed accesspoints iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 8080 -s $AP01 -j ACCEPT # UNIFI - AP01 iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 3478 -s $AP01 -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 8080 -s $AP02 -j ACCEPT # UNIFI - AP02 iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 3478 -s $AP02 -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 8080 -s $AP03 -j ACCEPT # UNIFI - AP03 iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 3478 -s $AP03 -j ACCEPT # log AP connections that aren't allowed iptables -N LOGDROP iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 8080 -j LOGDROP iptables -A LOGDROP -j LOG --log-prefix "IPTables-Dropped: " --log-level 7 iptables -A LOGDROP -j DROP # Make persistent iptables-save >/etc/iptables/rules.v4
Create a file in /etc/rsyslog.d/ called “30-unifi-accesspoints.conf” with the following content:
:msg,contains,"IPTables-Dropped: " /var/log/unifi_accesspoints.log
and restart rsyslog
Wednesday, May 13, 2020
Mediainfo with rar support
Mediainfo is a very nice utility, but it works even better with rar support.
Took me a while to compile it succesfully, therefor here are the steps. Easy once you know it :~
First, install current version of the normal Mediainfo and other requirements that we need later.
sudo -s apt install mediainfo libmediainfo-dev git build-essential
Then get the latest source code from the mediaarea.net website. Currently version 20.03.
mkdir /root/installers/ && cd /root/installers wget https://mediaarea.net/download/binary/mediainfo/20.03/MediaInfo_CLI_20.03_GNU_FromSource.tar.gz tar zxvf MediaInfo_CLI_20.03_GNU_FromSource.tar.gz cd MediaInfo_CLI_GNU_FromSource ./CLI_Compile.sh cd MediaInfo/Project/GNU/CLI && make install
Now we’re going to add the rar functionality. It depends on a modified version of libdvdread, also from lundman, that we need first.
cd /root/installers wget http://lundman.net/ftp/dvdread/libdvdread-4.2.0.plus.tar.gz tar zxvf libdvdread-4.2.0.plus.tar.gz cd libdvdread-4.2.0.plus ./configure && make && make install
And now we’re going to build the mediainfo-rar version:
cd /root/installers wget "http://www.lundman.net/ftp/mediainfo-rar/mediainfo-rar-1.4.0.tar.gz" tar zxvf mediainfo-rar-1.4.0.tar.gz cd mediainfo-rar-1.4.0 ./configure && make && make install
Run it: mediainfo-rar.
If it complains about “error while loading shared libraries: libdvdread.so.4”, fix it with:
ln -s /usr/local/lib/libdvdread.so.4 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libdvdread.so.4
That’s all.
Backup links in case sources will ever disappear:
MediaInfo_CLI_20.03_GNU_FromSource.tar.gz
libdvdread-4.2.0.plus.tar.gz
mediainfo-rar-1.4.0.tar.gz
Monday, May 11, 2020
DSM6: Run services like inetd in Synology debian-chroot
Somehow systemd does not run in the debian-chroot, so in case inetd is working for you, here’s how:
ssh to your synology
sudo -s chroot /volume1/@appstore/debian-chroot/var/chroottarget /bin/bash apt install wget tcpd zip unzip openssl lftp openbsd-inetd
Install software of choice. Then:
service openbsd-inetd start exit
Auto-start the inetd service with the debian-chroot:
sqlite3 /volume1/@appstore/debian-chroot/var/debian-chroot.db
INSERT INTO services VALUES ('0', 'INETD', '/etc/init.d/openbsd-inetd','ps -p $(cat /var/run/inetd.pid)');
.quit
DSM6: Create a Synology x64 debian chroot
1 Install the synology “noarch” package
Go to the Package Center, then Settings
Trusted sources, “Synology Inc. and trusted publishers”
Package Sources, Add, “SynoCommunity” + “http://packages.synocommunity.com/”
Community, install Python (v2.x, not v3) and nano
Manual Install, debian-chroot_noarch-all_8.4-7.spk but DO NOT “Run after installation”
2 Fix the DSM Interface
Ssh to your Synology
sudo -s cd /volume1/@appstore/debian-chroot/env/bin ./pip install click nano /var/packages/debian-chroot/target/app/debian-chroot.js
Then replace
"url": "3rdparty/debian-chroot/debian-chroot.cgi/direct/router", with "url": "/webman/3rdparty/debian-chroot/debian-chroot.cgi/direct/router", and: 'url': '3rdparty/debian-chroot/debian-chroot.cgi/direct/poller', with 'url': '/webman/3rdparty/debian-chroot/debian-chroot.cgi/direct/poller',
And alter the onclose function:
onClose: function () {
this.doClose();
this.mainPanel.onDeactivate();
return true;
},
3 Replace the binaries with x64
Remove old binaries:
cd /volume1/@appstore/debian-chroot/var rm -rf chroottarget
Put the x64 chroot.tar.gz in the current directory
tar zxvf chroot.tar.gz echo "chroot" >/volume1/@appstore/debian-chroot/var/chroottarget/etc/hostname cp /etc/resolv.conf /volume1/@appstore/debian-chroot/var/chroottarget/etc/resolv.conf touch /usr/local/debian-chroot/var/installed
If you created a chroot for a different architecture than x64, use the following command. Otherwise skip this.
chroot /volume1/@appstore/debian-chroot/var/chroottarget /debootstrap/debootstrap --second-stage
The chroot is now installed. Start it:
/var/packages/debian-chroot/scripts/start-stop-status start
Enter the chroot:
chroot /volume1/@appstore/debian-chroot/var/chroottarget /bin/bash
Post-installation steps:
apt update && apt upgrade && apt autoremove apt-get install locales dpkg-reconfigure locales -> only "[*] en_US.UTF-8 UTF-8" -> system default: en_US.UTF-8 dpkg-reconfigure tzdata -> set correct timezone, e.g. Europe, Amsterdam
Optional
If you want extra mounts in your chroot, look in:
/var/packages/debian-chroot/scripts/start-stop-status
example to add a Synology share called stuff to the chroot:
add to BOTTOM of all mount commands in section start_daemon script:
grep -q "${CHROOTTARGET}/mnt/site " /proc/mounts || mount -o bind /volume1/stuff ${CHROOTTARGET}/mnt/site
add to TOP of all umount commands in section stop_daemon script:
umount ${CHROOTTARGET}/mnt/site
Reboot your synology
Create debian x64 chroot files (for Synology debian-chroot)
On your current installed debian x64 installation:
sudo apt install debootstrap sudo debootstrap stable chroottarget sudo tar -cvzf chroot.tar.gz chroottarget
Save the chroot.tar.gz
The above creates a debian chroot. Here’s how to make an Ubuntu one. jammy is currently the latest LTS:
debootstrap jammy chroottarget/ http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/
If you need to create a chroot for a different architecture, eg armhf, the second command would be:
sudo debootstrap --foreign --arch armhf stable chroottarget
Thursday, October 10, 2019
Win 10 slow startup caused by AMD Radeon graphics card
Reminder: Look in registry for EnableUPLS and set 1 to 0.
Thursday, July 18, 2019
Save and re-install debian/ubuntu packages
save current installed packages to textfile
dpkg -l | grep ^ii | awk '{print $2}' > installed.txt
re-install packages from textfile
sudo apt-get install $(cat installed.txt)